MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) is an additive manufacturing technology developed by HP Inc. It is a 3D printing process that can produce functional nylon prototypes and end-use production parts in 1 day and involves layering Powdered thermoplastic materials to quickly create complex parts. The final part has a high-quality surface finish, excellent feature resolution, and more consistent mechanical properties, which significantly increases productivity and reduces costs compared to processes such as selective laser sintering.
MJF process printing process
- MJF uses an inkjet array to deposit flux onto a powder material (usually a thermoplastic polymer) and distribute it over a build platform to selectively apply fixer and refiner, which are then melted into a solid layer via a heating element.
- After each layer is printed, the heating element passes across the entire bed, causing the powder material to melt and solidify. The process is then repeated until the part is completed. It produces final products quickly, robustly and with a high level of detail.
- After printing is complete, the entire powder bed with encapsulated parts is moved to a vacuum processing station, where most of the loose powder is removed by integrated vacuum.
- The parts are shot blasted to remove residual powder, and then sent to the processing department for dyeing or secondary processing.
Features of MJF
The most special thing about MJF is that it allows designers to achieve the desired shape without the constraints of the manufacturing process, while still meeting the required strength, uniformity and robustness of the final product. In addition, MJF is designed for mass production, ensuring high production efficiency even in high-volume production, while always maintaining high-quality parts. By combining MJF’s unique manufacturing methods with the capabilities of 3D printing technology, it brings new value to the manufacturing and creative industries.
Key advantages of MJF include:
- Ability to mass produce customized products.
- Only 3D data is needed to quickly transition to the production process.
- Manufacturing from prototype to final product without traditional factories.
- Compared with traditional cutting or injection molding methods, the cost is reduced and the delivery time is shortened.
- Ability to produce complex shapes into single pieces, reducing assembly work.
- This process can simplify the work process and reduce costs, achieve rapid prototyping, and realize parts manufacturing with breakthrough economic benefits.
- An open material and software innovation platform that lowers the threshold for use and supports new applications in various industries.
- MJF 3D printing can produce end-use parts with near-isotropic properties on demand, and the performance consistency of the products is good.
- The printing speed for small batch orders is fast, and the overall cost is competitive.
- Materials are highly reusable. For example, PA12 only requires additional materials when it is reused in the next production.
- High air tightness, making it suitable for producing leak-free parts and pneumatic applications.
Disadvantages of MJF
- MJF can be cost-effective in terms of manufacturing costs of parts, but the equipment acquisition cost is relatively high, which may result in higher overall costs depending on the printing frequency. Printer prices may vary depending on model and configuration as well as any other accessories or options.
- Unable to produce some curved, hollow geometries
- Requires proprietary materials
Commonly used MJF 3D printing materials are as follows:
PA12W (white): white nylon material, with excellent noise and vibration damping properties, beautiful design and wear resistance, suitable for various environments.
PA12GB (Glass Beads): A reinforced nylon material of PA12 that has higher stiffness than PA12 and adds glass beads.
PA12: A versatile, low-cost nylon material with excellent strength and physical properties that can be used in a variety of applications.
PA11: A plant-derived nylon material with excellent flexibility and higher toughness compared to PA12.
MJF post-processing methods
MJF does not require support structures (structures that are only used to support the object during the printing process and are later removed), making post-processing relatively simple. MJF leaves unused powder material around the printed object to act as a support. This eliminates the need for special materials or structures dedicated to support. Therefore, the desired shape can be created based on the designer’s original design. After the cooling stage, the remaining powder is removed by processes such as sandblasting, air blasting or water blasting.
MJF industry applications
MJF is unique in its application in high-standard industries such as the automotive industry and medical technology as well as consumer goods.
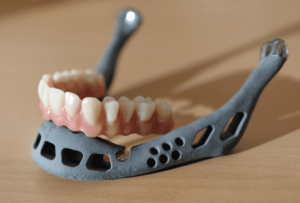
Dental/Medical Industry: The medical and dental industry is experiencing an explosion of 3D printing applications and large-scale personalized products. SmileDirectClub in Nashville, Tennessee has 60 HP Multi Jet Fusion printers working around the clock to create custom dental molds; HP Jet Fusion 3D printers are also changing the orthotics industry and enabling the production of customizable medical prostheses; Invent Medical uses HP white PA12 Manufacturing of custom orthotics and prosthetic devices, personalized appliance prototypes – Orthodontic appliances (mouthpieces) must be individually designed for each patient’s oral environment.
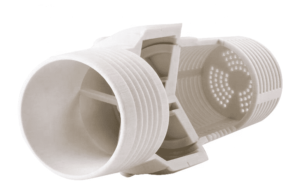
Manufacturing (Automotive & Industrial Equipment): Cooling Duct Components – This is an example of a cooling duct installed inside an HP printer. Parts previously manufactured by assembling six parts and screws have been integrated and manufactured into a shape that reflects the results of analysis to produce optimal airflow. This reduces manufacturing costs by 34% and increases airflow by 22%. MJF 3D printing is helping automobile and vehicle manufacturers reduce component production costs while improving operational efficiency. A Spanish auto parts supplier (Continental Automotive Spain SA) uses MJF printing to develop pneumatic fixtures to shorten the processing time of new parts. At Jaguar Land Rover, automotive engineers are using HP Multi Jet Fusion to develop next-generation protective equipment for factory workers; General Motors’ new 15,000-square-foot Additive Industrialization Center incorporates HP MJF machines into its fleet of 3D printers to produce prototype parts, tools , fixtures and end-use parts.
Aerospace Industry: Prototypes – PA12GB MJF 3D printing can even be used for their satellite prototypes. 3D printed objects are used not only to check mechanical designs but also as communication tools with internal members.
Consumer Products: Many types of consumer products require the production of low-volume, complex-shaped parts. Eyewear is one of the fastest growing consumer product categories manufactured using HP Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing.
Multi-jet fusion (MJF) is a relatively new technology in the field of 3D printing, but in just a few years, MJF has begun to move toward industrialization. Today, MJF is widely used by manufacturers as a reliable part manufacturing technology for a variety of products, including automotive parts, factory tools, orthopedic braces, and consumer products.

 Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Español
Español



